CAD Drawing File Types: STEP vs STL
When creating CAD files, choosing the right file type is crucial for ensuring that your design can be easily shared, modified, and used for its intended manufacturing application. Different companies have different preferences, so it’s essential to understand the differences between common CAD file types. This article focuses on STEP and STL files, helping you make informed decisions when requesting or creating a CAD model for direct applications.
Understanding Manufacturing File Types
Manufacturing CAD files fall into three major categories: native file types, neutral file types, and 3D printing file types. Each category serves specific purposes and has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Native File Types
Native file types are the default proprietary file types used by different CAD programs. Examples include SolidWorks part files (SLDPRT), Creo and AutoCAD part files (PRT), and AutoCAD native files (DWG and DSF). These files are rich in data and highly efficient for making modifications. For instance, a SolidWorks part file includes a feature tree, which allows engineers to see how the original drafter created the part and make specific changes without extensive rework.
However, native file types have limited compatibility with other CAD software, which can hinder design collaboration with other companies. If someone sends a native file, it often requires the same CAD program software to open and modify it, potentially blocking seamless integration with other design and engineering teams.
Neutral File Types
Neutral file types, like STEP files, are designed to be universal and usable across different CAD software. A STEP file retains detailed information about the design, allowing it to be measured, modified, and used for simulations such as Finite Element Analysis (FEA) or Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). These files are essential for collaboration between design companies, mold companies, and toolmakers.
The primary advantage of STEP files is their compatibility across various platforms, making them ideal for collaborative projects. However, when a native file is saved as a STEP file, the feature tree is dissolved, losing the step-by-step instructions on how the part was designed. Any modifications must be made as if the part is a foreign body with no references, and conversion errors can occasionally occur, necessitating a thorough review to ensure accuracy.
3D Printing File Types
3D printing file types, such as STL and AMF, are used in slicing software that prepares the commands for 3D printers. These files convert the solid body into a mesh of individual triangles, ready for 3D printing. STL format files are widely used due to their simplicity and compatibility with most 3D printing software.
The advantage of the STL file format is its ease of use for direct printing, and it can be created in non-engineering 3D modeling software like Blender. However, these files do not allow for detailed analysis or modifications. They cannot be evaluated as solid bodies, meaning no FEA or CFD analysis can be performed, and they are not suitable for precise engineering requirements.
What is a STEP File?
STEP (Standard for the Exchange of Product model data) is a neutral CAD file format that enables the exchange of data between different CAD programs. It is designed to be universal, allowing for seamless collaboration across various engineering platforms. STEP files contain detailed information about the geometry and structure of the design, making them ideal for comprehensive evaluations and modifications.
One of the key benefits of the STEP file format is its ability to retain detailed design information, which is crucial for simulations and analysis. For example, engineers can use STEP files to conduct FEA simulations to assess the structural integrity of a part or CFD simulations to evaluate fluid flow and thermal dynamics. This level of detail makes STEP files indispensable for ensuring that a design meets all application requirements.
Toolmakers and mold companies often require designs to be in STEP format due to their compatibility and detailed information. However, it’s important to note that when a native file is converted to a STEP file, the feature tree is lost, and any modifications must be made without the original design references.
What is an STL File?
STL (Stereolithography) is a file format widely used in 3D printing. Unlike solid or neutral files, STL files represent a mesh of individual triangles that approximate the surface of the 3D model. This mesh structure is essential for slicing software, which generates the layer-by-layer instructions needed for 3D printing.
The simplicity and ease of use of STL files make them popular for rapid prototyping and additive manufacturing. They can be created in various 3D modeling software, making them accessible to a broad range of users, including those without engineering backgrounds. However, the mesh structure of STL files means that they lack the detailed information necessary for precise engineering analysis.
STL files cannot be evaluated as solid bodies, and they are unsuitable for FEA or CFD simulations. Additionally, toolmakers do not accept STL files for tooling or mass production, as these files do not provide the necessary data for accurate manufacturing.
STEP vs STL: A visual comparison
At this stage, IMS produces your fully functional, optimized parts at scale, ready for use in their intended applications. During the injection molding process, we ensure optimal cycle times to keep your project on time and on budget. We also offer a range of post-process services, including insert molding, pad printing, and parts assembly.
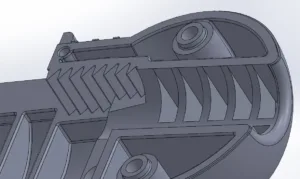
Example of a smooth STEP file

Example of a meshed STL file
Converting STEP to STL: Can it be Done?
Converting a STEP file to an STL file is straightforward and commonly done to prepare models for 3D printing. The conversion process involves creating a mesh from the detailed geometric data in the STEP file. This mesh is then used by slicing software to generate the instructions for the 3D printer.
The advantage of converting STEP files to STL is that it retains the overall shape and dimensions of the original design, ensuring accurate 3D prints. However, the conversion process also simplifies the surface geometry, which can lead to a loss of detail in the printed part.
Converting STL to STEP: Can it be Done?
While it is technically possible to convert an STL file back to a STEP file, this process is not recommended. The mesh structure of STL files lacks the detailed design data necessary for a smooth and precise conversion. The resulting STEP file will not have the original design’s integrity, making it unsuitable for detailed engineering analysis, injection molding, or other manufacturing processes.
If you only have an STL file and need a STEP file for molding or other precise applications, it’s better to reverse engineer the part or request the original designer to provide a STEP file. Converting an STL file to a STEP file results in a loss of precision and smoothness, which can compromise the quality and functionality of the final product, particularly for precision parts or parts with complex shapes or complex geometry.
What to send to IMS
When sending CAD models to IMS, a neutral STEP file is preferred due to its compatibility and detailed information, which facilitates collaboration and thorough evaluation. If only native files are available, confirm with IMS that the format is compatible with their software. IMS can use 3D printing files solely for 3D printing purposes; these files cannot be measured, evaluated, or quoted for molding or tooling.
Understanding the appropriate use cases for STEP and STL files ensures a smoother manufacturing process and helps avoid unnecessary complications and delays. By choosing the right file type early in your design process, you can streamline your project from start to finish, ensuring high-quality and precise manufacturing outcomes. Contact us today to get started.






