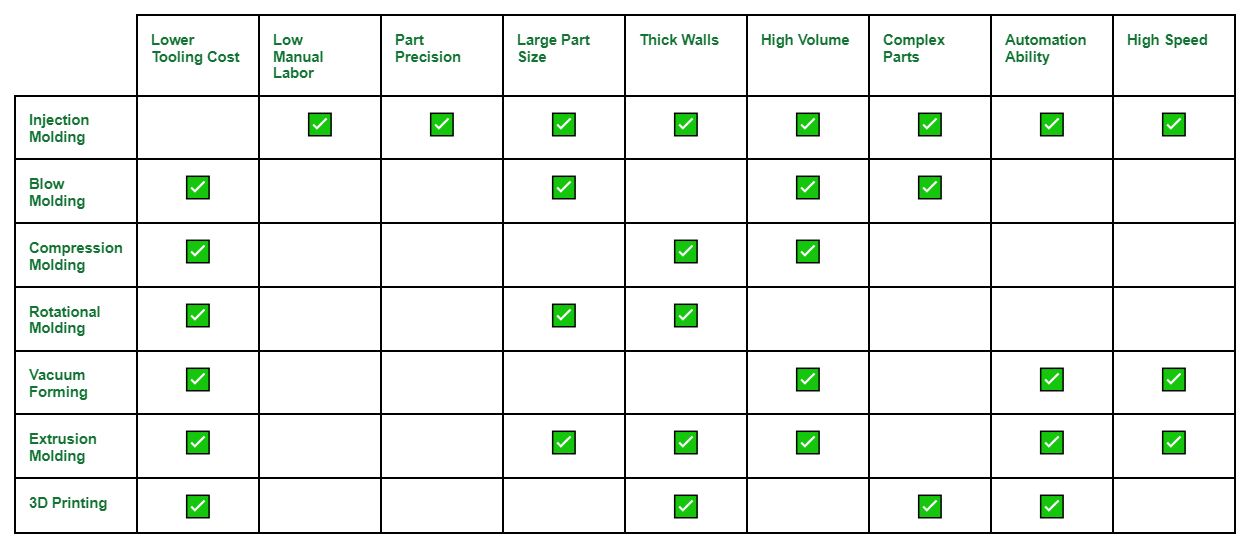
 Plastic manufacturing encompasses a wide variety of techniques, each suited to different requirements and plastic part specifications. Factors such as part thickness, volume, complexity, tooling cost, and plastic component size constraints play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate manufacturing process.
Plastic manufacturing encompasses a wide variety of techniques, each suited to different requirements and plastic part specifications. Factors such as part thickness, volume, complexity, tooling cost, and plastic component size constraints play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate manufacturing process.
Integrated Molding Solutions (IMS) is a plastics manufacturer specializing in plastic injection molding and 3D printing processes. In this plastic fabrication article, we will explore the different plastic manufacturing methods and how they compare to injection molding.
Overview of Injection Molding
To best understand the different plastic production comparisons, let us begin with a brief overview of injection molding. Injection molding is a highly versatile process suitable for precise, high-volume manufacturing of complex parts. It involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity, where it quickly solidifies to form the desired shape. Injection molding is preferred for parts requiring precision, automation, and high-volume production.
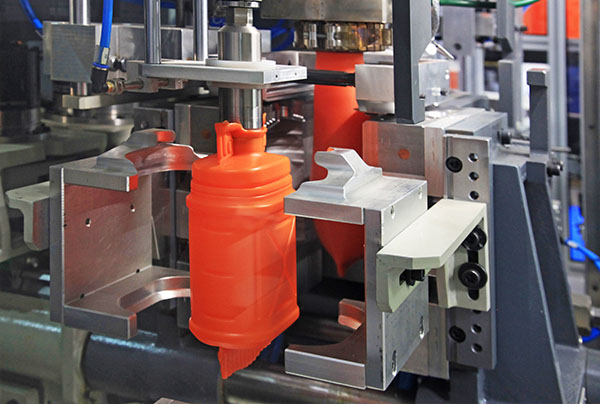 Blow Molding Vs. Injection Molding
Blow Molding Vs. Injection Molding
Blow molding is a plastic manufacturing process best suited for producing hollow plastic parts like containers and bottles, which are characterized by thin walls. The process involves dropping a preform between two mold halves, which are then closed to form the outer walls of the part. Subsequently, the preform is inflated with air to fill the cavity, resulting in thin-walled structures.
Pros and Cons of Blow Molding
Blow molding offers advantages such as lower tooling and manufacturing costs compared to injection molding. It allows for the creation of thin walls and varying internal geometries that may be expensive or impossible with injection molding. However, drawbacks to injection blow molding include limitations to hollow and thin parts, less precision, and the need for manual trimming and cleanup due to flash formation.
Compression Molding Vs. Injection Molding
Compression molding is another manufacturing technique used for simpler parts such as gaskets and shoe soles. This plastics manufacturing method involves heating a preformed sheet of raw material vertically between two mold halves, which are then pressed together to form the desired shape under both temperature and pressure.
Pros and Cons of Compression Molding
Compression molding offers lower tooling and process costs compared to injection molding and allows for the use of raw material like rubber, which is a challenging material to injection mold. However, it is less precise, requires more manual labor, and entails additional plastic waste and cleanup due to flash formation as compared with injection molding.
Rotational Molding Vs. Injection Molding
Rotational molding, or roto-molding, is ideal for producing large hollow containers such as storage tanks. In the rotational molding process, polypropylene or polyethylene powder is placed into a mold, which is then heated and constantly rotated on two axes. This heating combined with the rotating mold and gravity allows the melted plastic powder to form the container’s walls. This process is slower than injection molding but can produce large, one-piece, hollow geometries.
Pros and Cons of Rotational Molding
Rotational molding offers tooling cost advantages and the ability to create one-piece, large hollow geometries. Roto molds are typically made from less expensive aluminum, as opposed to the more costly steel from which injection molds are made. However, rotational molding is less precise, slower, and requires manual trimming and cleanup as compared to injection molding.
Vacuum Forming Vs. Injection Molding
Vacuum forming or vacu-forming, is suitable for thin parts but has limitations compared to injection molding. Vacuum forming involves heating a thin plastic sheet and using vacuum pressure to form it around a mold. While it offers cost advantages and the ability to create thin parts, it is not a suitable manufacturing process for thicker plastic parts and plastic product complexity.
Pros and Cons of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming offers more cost-effective tooling for thin parts but has limitations in thickness and plastic part complexity compared to injection molding. It is a cost-effective option for prototyping components at a low volume, whereas injection molding is preferred for high-volume part runs.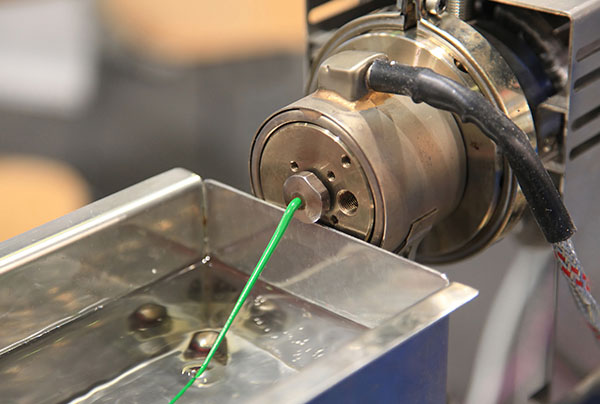
Extrusion Molding Vs. Injection Molding
Extrusion molding is suitable for creating parts like tubes, PVC pipes, and straws, but has limitations compared to injection molding. Plastic extrusion involves pushing melted plastic pellets through a die to form the desired shape of the plastic piece. While it offers cost advantages in the tooling stage and the ability to create long parts, it is limited to two-dimensional designs.
Pros and Cons of Extrusion Molding
Extrusion plastic molding is cost-effective for long parts but is limited to two-dimensional designs and produces weaker parts compared to injection molding. Additionally, extrusion molded plastic parts often vary in size because of die swell.
3D Printing Vs. Injection Molding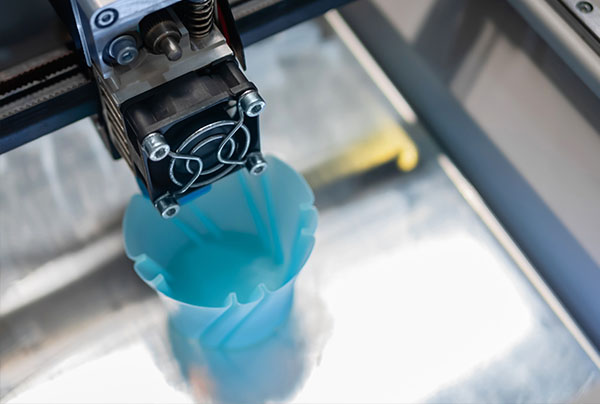
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves layer-by-layer deposition of plastic material to create three-dimensional objects based on digital designs. It offers flexibility in design iterations and customization, making it suitable for prototyping and low-volume production.
Pros and Cons of 3D Printing
One major advantage of 3D printing is its ability to produce complex geometries with minimal tooling requirements. It also allows for rapid prototyping and customization. However, 3D printing is significantly slower and more expensive than injection molding for high-volume production. Additionally, the available plastic material options for 3D printing are currently more limited compared to injection molding material options. More information about the differences between custom injection molding and 3D printing can be found here.
How Injection Molding Stacks Up For Plastic Manufacturing
Injection molding excels in precision, automation, and producing finished parts without the added time and labor of secondary processes. However, it may not be suitable for all geometries or plastic materials, and it typically involves higher tooling costs compared to blow molding.
Injection molding remains the preferred choice for precise, high-volume manufacturing of complex parts with minimal manual intervention. Its advantages include precision, automation, and the ability to produce finished parts without secondary processes. At IMS, we specialize in helping clients optimize their designs for injection molding to achieve the best results.
IMS: Your Injection Molding Leader in the Plastics Industry
IMS stands out as a leader in the plastic manufacturing industry, recognized for its commitment to quality, timely delivery, and value. With more than 20 years of experience, our plastics company operates a range of advanced injection molding machines and 3D printers, equipped to handle a wide range of plastic manufacturing requirements.
Our team of industry veterans and top professionals is dedicated to providing end-to-end solutions, from initial design and 3D printed prototyping to the completion of the molding process. Choose IMS for your plastic injection molding needs and benefit from our expertise and precision. For top-tier plastic manufacturing services, contact Integrated Molding Solutions today.