Commercial 3D Printer Capabilities
Today’s commercial 3D printers produce technologically advanced parts with a massive range of applications. 3D printing is a time-efficient and cost-effective method for producing single plastic parts or small batches of parts. Two leading 3D printing technologies in which Integrated Molding Solutions specializes are PolyJet 3D printing and fused deposition modeling (FDM 3D Printing).
How are FDM 3D Printing and PolyJet 3D Printing Similar?
In some aspects, FDM 3D printing and PolyJet 3D printing are comparable. Both PolyJet 3D printers and FDM 3D printers have similar size constraints. However, for parts that exceed the size capacity of the 3D printer, IMS utilizes our extensive plastic design experience to engineer two or more pieces that snap, click, epoxy, or solvent-weld together. With IMS’s parts assembly services, these types of connective, 3D-printed parts are both strong and functional solutions.
Both FDM 3D printing and PolyJet 3D printing work well for printing short runs of parts, in which the needed quantity does not justify the cost of building an injection mold. For larger batches of plastic parts that require injection molding, 3D printing allows for fast and accurate prototyping. A 3D printed prototype enables hands-on assessment of the design before molding and can be easier to evaluate than digital material such as CAD models, CAD drawings, or a GrabCAD print. Prototyping a part before designing an injection mold is often a wise financial investment. Evaluating 3D printed prototypes ensures that any necessary part design changes are made before designing and building an expensive injection mold.
There are a number of key differences between FDM 3D printing and PolyJet 3D printing, which should be considered before deciding between the two methods. First, let’s look at the unique characteristics of each 3d-printing type.
What Is FDM 3D Printing?
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is 3D printing technology in which a filament of thermoplastic is extruded from the printer in two-dimensional layers to build up a plastic part. The filament is fed from a spool through a heated printer head, which deposits layer by layer of plastic onto the build tray until the design is complete.
The Benefits of FDM 3D Printing
FDM printed parts are strong and functional. FDM 3D printing is ideal for basic, low-cost prototyping of simple parts or early-stage conceptual models. Thermoplastic filaments used in FDM printing are significantly less expensive than the materials used in PolyJet 3D printing or in selective laser sintering. The cost-effectiveness of the multiple materials used in FDM filaments makes this 3D printing service a sound choice for tight budgets.
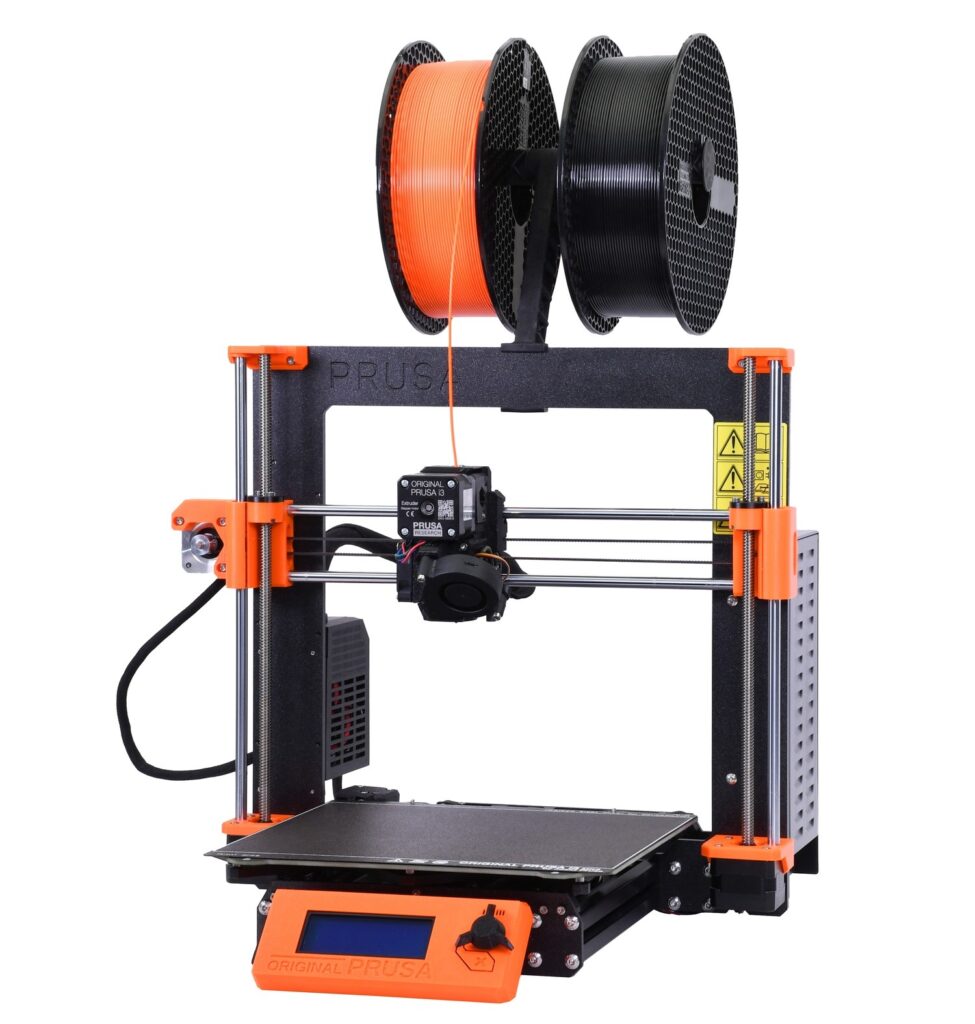
IMS engineers are experts at plastic design for FDM 3D printing to prevent delamination, or separation along layer lines. At IMS we use commercial-grade Prusa printers, which is a premier brand of the highest quality FDM printers. This technology combined with our plastic expertise allows us to print FDM parts that have the strength of injection molded parts. With our FDM commercial 3D printing capabilities, IMS is able to print more precise parts with a higher resolution surface finish than a desktop FDM machine.
FDM 3D Printing Materials
There are a wide variety of thermoplastic material options for FDM filament. Each type of thermoplastic filament has its own unique features. IMS engineers use their expertise to select the material that is best for the form, fit, and function of the plastic part.
- PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable bio-sourced material made from corn husks and sugar beets. Using PLA filament in FDM 3D printing is a sustainable choice, as the part will degrade and eventually decompose if exposed to sun or rain. PLA filament is inexpensive and ideal for printing functional prototypes. 3D printing with PLA filament creates parts that are both stable and structurally sound without being solid all the way through. This allows for the printing of larger parts with less material, further increasing the economic benefits of PLA filament.
- ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is another filament option for FDM 3D printing. ABS filament is ideal for concept models and form-focused prototypes, as it is lighter and tougher than PLA.
- PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol) is a thermoplastic polyester that is useful for waterproof applications. It is available in transparent grades and is chemical and moisture resistant, making it ideal for food-safe plastic parts.
- Nylon filament is known for its high temperature resistance and durability. It’s one of the more challenging filament materials to use in an FDM 3D printer but is beneficial for functional prototypes because of its strength and partial flexibility.
- TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) is an even more flexible material. For parts that are designed to be flexible, stretchy, or vibration-dampening, TPU is an ideal filament choice.
- PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) is used as a support material in FDM 3D printing. For parts that are designed with an overhang, a support structure made of support material is needed so the FDM printer can lay down the overhanging layer. PVA is a water soluble material that is ideal for this purpose.
- HIPS (high impact polystyrene) is another support material used in FDM 3D printing. HIPS filament is most commonly used in combination with ABS filament. It is not water soluble, but dissolves in chemical limonene.
- Composite filaments (e.g., certain grades of material with kevlar, carbon fiber, fiberglass fillers) are more expensive than other FDM filament materials. They are extremely useful, however, for tough, functional prototypes. Composite filaments are only compatible with commercial-grade FDM printers, not with hobbyist FDM printers.
When to Use FDM 3D Printing
Advances are rapidly being made in filament material technology. Thermoplastic materials previously only available for injection molding are now able to be FDM 3D printed. This allows the part to function nearly as if it were injection molded with the precision of a 3D printer. FDM 3D printed parts are generally hollow with an intricate internal lattice of thin walls that add strength to the part. Because of this internal honeycomb-like design, well-designed FDM 3D printed parts can be stronger than PolyJet 3D printed parts.
FDM 3D printing is the less expensive additive manufacturing option when it comes to producing low volumes of parts. The cost of thermoplastic filament is less than the cost of liquid photopolymer. Cost-effectiveness makes FDM 3D printing the right choice for prototypes or small batches of parts that require function and mechanical strength over form or aesthetics.
What is PolyJet 3D Printing?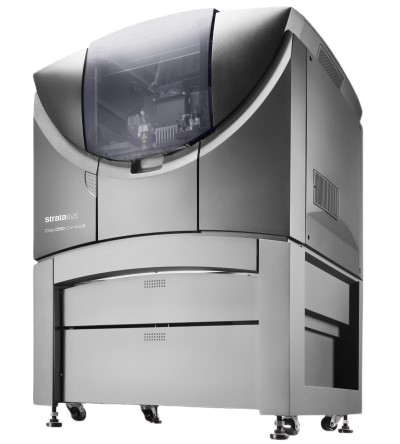
PolyJet 3D printing is a more complex form of printing than FDM and uses an entirely different material than FDM 3D printing. PolyJet technology uses two or more jet heads to spray a liquid photopolymer, or liquid plastic, onto the build tray in extremely thin layers. Each photopolymer layer is cured and hardened by a UV light in the PolyJet printer before the next layer is added. PolyJet technology is similar to that used in inkjet printing. This additive manufacturing method allows for a significantly higher resolution, or surface accuracy, than FDM printers or SLA 3D printers. We utilize Stratasys Objet connex 3D printers for our PolyJet 3D printing service at IMS.
The Benefits of PolyJet 3D Printing
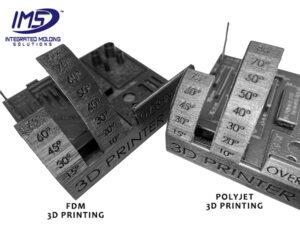
Individual PolyJet layers are 16-36 μm (micrometers) in height. This is equivalent to 0.016-0.036 mm. For comparison, each layer printed by an FDM 3D printer is 0.15-0.2 mm. Because of this layer height, an FDM 3D printed model or part often has a pixelated or stepped appearance. PolyJet printers 3D print parts with significantly higher resolution, which makes PolyJet printing an ideal choice for rounded parts and form-focused prototypes.
A PolyJet 3D printer makes alloys as it prints, which allows the emulation of characteristics of a wide variety of plastics. With PolyJet technology, IMS is able to match the mechanical properties of almost any type of plastic. PolyJet 3D printing technology allows multiple materials to be printed on the same part. Overhang in plastic part design is also not an issue with PolyJet 3D printing. PolyJet printing uses a water-soluble support material that encases the part to provide support. As part of our PolyJet 3D printing service, IMS has a specialized wash bath and water jet station to remove this support material and clean each PolyJet part.

Photopolymer 3D Printing Materials
Photopolymer materials used in PolyJet printers vary widely in color, texture, Shore Hardness, or indentability of a material. The versatile material properties of photopolymers make them ideal for complex shapes and realistic prototypes.
- RGD720™ is a translucent, rigid photopolymer that is ideal for parts that require high stability and surface smoothness.
- DraftGrey™ is one of the most cost-effective photopolymer options and is useful for concept prototypes.
- Tango™ photopolymer is used to print non-slip surfaces or soft-touch coatings for realistic prototypes. It can range in shore hardness and is the material used to make flexible prototypes.
- Vero™ photopolymer comes in a vast array of colors. It is rigid, opaque, and combines fine detail with versatile strength, making it ideal for prototypes with complex geometries.
- Digital ABS Plus™ is a curable liquid photopolymer that is both strong and resistant to high temperatures. It is ideal for realistic, precise prototypes or parts.
- Durus™ and Rigur™ are two high-quality simulated polypropylene photopolymers. They are useful for parts that need to be both durable and smooth.
- High Temperature photopolymer material is ideal for static parts that need to be heat resistant.
- Agilus30™ photopolymer is rubber-like and capable of repeated bending without breakage or tearing.
- PolyJet support materials are water soluble and used to support the part during 3D printing. These materials are removed by water baths or water jets after printing.
Photopolymer Materials for Medical Applications
Many photopolymers are human-contact grade, making them ideal for plastic parts used in medical fields.
- DraftWhite™ is most commonly used for single-material medical applications like those used in orthopedics.
- TissueMatrix™ is the softest commercial-grade photopolymer. It behaves like human tissue and is used for a number of applications in medicine.
- BoneMatrix™ is both tough and flexible. Its porous structure mimics that of human bone.
- GelMatrix™ is a soft photopolymer that is useful for printing complex vascular structures.
- RadioMatrix™ is used to print medical models that behave realistically under x-rays or CT scans.
- Dental materials used in PolyJet 3D printing allow for highly accurate dental models as well as for human-contact grade parts for dental procedures.
Photopolymers in Commercial 3D Printing
With so many types of photopolymers, commercial PolyJet 3D printing is the additive manufacturing technique that is most applicable for a wide variety of industries. Photopolymer applications range from 3D printed realistic models of gums and teeth used in dental schools to the soles of hiking boots designed to scale mountains. PolyJet materials can be used to model anatomically correct parts for surgical training and to print castable molds for jewelry. Photopolymers are becoming increasingly ubiquitous in commercial 3D printing because of their incredible versatility.
When to Use PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet 3D printing allows for smooth surface finishes and an array of texture and hardness options. Liquid photopolymers are sprayed in such thin layers during PolyJet 3D printing that the surface of even a curved or rounded part can be almost perfectly smooth. PolyJet 3D printing eliminates the issue of layer lines or steps on part surfaces, which can be an issue with other 3D printing technology. For parts that are smaller in size, PolyJet 3D printers can print multiple in a row. For projects with higher volumes, PolyJet 3D printing is often more economical than FDM.
More complex designs for plastic parts are possible with PolyJet 3D printing. The PolyJet 3D printer encases parts with a water-soluble support material, which allows parts to be designed with geometric overhangs and other complex features. This support material is then removed with a water bath or a water jet, leaving the photopolymer part clean.
Get help selecting which 3D printing material and method fits your needs!
Integrated Molding Solutions has decades of plastic manufacturing experience, including material selection, part design, and environmentally sustainable resources. Let us guide you through the plastic fabrication process as you grow from prototypes to mass production of plastic parts. Join us in our mission to provide environmentally responsible plastic products to grow businesses and leave a positive impact on the world. Contact IMS today for a 3D printing services consultation.