A Comprehensive Look at the Chemical Resistance of Plastic Materials.

Plastic manufacturing offers versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness through the wide selection of plastic materials. Understanding the chemical resistance of plastics is essential to ensure their performance and longevity in diverse applications. In this IMS plastic resource article, Integrated Molding Solutions discusses plastic materials’ chemical resistance, providing valuable insights for engineers, designers, and manufacturers.
Understand the chemical resistance of plastics.
A plastic material’s chemical resistance refers to the material’s ability to withstand exposure to different chemicals without developing degradation or damage. Plastics exhibit varying degrees of chemical resistance, depending on factors such as their molecular structure, composition, and processing techniques. Identifying the product’s specifications will be vital to evaluate a plastic material’s resistance to specific chemicals to ensure its suitability for a given application.
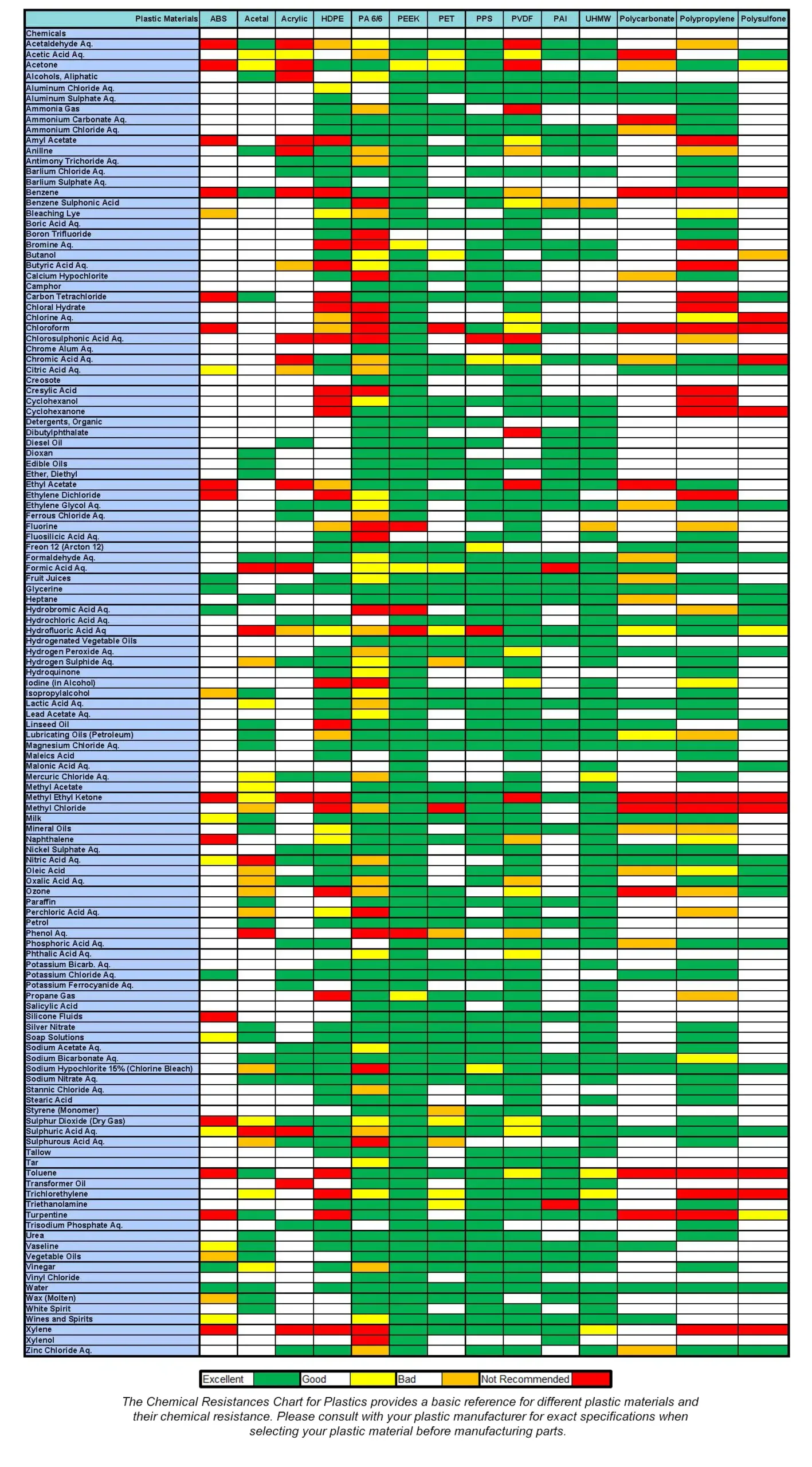
Chemical Resistance Chart for Plastics:
Several factors that influence the chemical resistance of plastics:
 Plastic Polymer Type:
Plastic Polymer Type:
The type of polymer used in plastic manufacturing is a primary factor in its chemical resistance. Different polymers have unique molecular structures and chemical compositions that dictate their interactions with various chemicals. For example, fluoropolymers like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, and perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) are known for their exceptional chemical resistance due to the strong carbon-fluorine bonds in their molecular chains. These polymers exhibit inert behavior and are resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and corrosive chemicals.
Chemical Resistant Plastic Additives and Fillers:
Additives and fillers are often incorporated into plastic materials to enhance specific properties such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, and mechanical strength. However, incorporating additives and fillers into your plastic material can also affect the material’s chemical resistance. Some additives may react with certain chemicals, leading to degradation or loss of performance. Additionally, fillers can create pathways for chemical penetration, compromising the material’s resistance. It’s essential to carefully consider the type and concentration of additives and fillers when selecting a plastic material for chemical-resistant applications.
Molecular Structure of the Plastic Material:
The molecular structure of a plastic material plays a crucial role in its chemical resistance. Polymers with tightly packed molecular chains typically have higher chemical resistance because they offer fewer points for chemical penetration. On the other hand, polymers with a more open molecular structure may be more susceptible to chemical attack. For example, linear polymers like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) have relatively dense molecular structures that provide excellent resistance to chemical penetration, making them suitable for applications in harsh chemical environments.
Injection Molding or Plastic Manufacturing Process Conditions:
The conditions used during injection molding or other plastic manufacturing processes can influence the chemical resistance of the finished plastic product. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and curing time can affect the plastic material’s molecular structure, crystallinity, and chemical properties. For example, high-temperature processing methods like injection molding and extrusion can cause molecular chain orientation and alignment, resulting in improved chemical resistance. Conversely, inadequate processing conditions or improper curing can lead to defects and weaknesses in the material, making it more susceptible to chemical attack. Therefore, optimizing the plastic manufacturing parameters is essential to ensure the desired chemical resistance of plastic products.
The chemical resistance of plastics is just one of many important factors to consider early in the manufacturing process.
Plastic manufacturers like Integrated Molding Solutions assist by considering these factors when selecting plastic materials for applications that require chemical resistance. Whether it’s choosing a fluoropolymer for aggressive chemical environments or selecting additives to enhance a material’s resistance to specific chemicals, understanding the factors influencing chemical resistance is crucial for achieving optimal performance and durability in various applications.