Enhancing Injection Molding with Plastic Additives and Fillers
 Injection molding is a highly versatile and widely-used manufacturing process in which molten plastic is injected into a mold to create a wide range of products and components. Most importantly, the properties and characteristics of the final plastic product can be significantly influenced by the plastic additives and fillers combined into the plastic polymer / raw material. These polymer additives are mixed with the base resin to enhance various material properties. In this article, we will delve into the world of plastic additives and fillers for injection molding, exploring their types, functions, and the benefits they bring to the manufacturing process.
Injection molding is a highly versatile and widely-used manufacturing process in which molten plastic is injected into a mold to create a wide range of products and components. Most importantly, the properties and characteristics of the final plastic product can be significantly influenced by the plastic additives and fillers combined into the plastic polymer / raw material. These polymer additives are mixed with the base resin to enhance various material properties. In this article, we will delve into the world of plastic additives and fillers for injection molding, exploring their types, functions, and the benefits they bring to the manufacturing process.
What Are Plastic Additives and Fillers?
Plastic additives and fillers are compounds that are introduced into the base resin, which forms the foundation of the plastic material.
Understanding Plastic type and Additives and Fillers
These compounds serve a variety of purposes, including altering the material’s physical properties like UV or chemical resistance, enhancing its appearance like color or texture, and improving its performance characteristics like increasing strength and durability. Plastic polymer additives and fillers can be incorporated into the plastic through two main methods: by having the material manufacturer compound them into the base resin or by adding them as concentrates during the molding process.
Types of Plastic Additives and Fillers
Colorants:
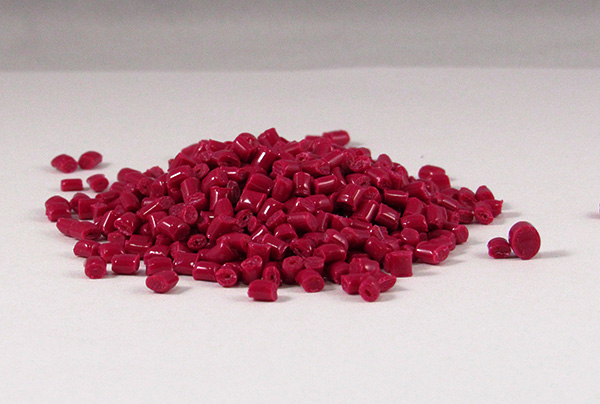
One of the most common additives, colorants are concentrated colors used to change the color of the plastic polymer. Colorants are available as off-the-shelf choices in the form of masterbatches. These masterbatches are highly concentrated and are mixed with the base resin at specific ratios, known as let-down ratios, to achieve the desired color. Custom colors can also be created based on Pantone colors or other color identification systems. Colorants can enhance plastic consumer goods or finished products with capabilities including; glowing under UV light, changing color in hot water, or fluorescent or metallic color effects.
Plasticizers:
Plasticizer additives reduce the intermolecular forces within the polymer, increasing the material’s flexibility. They are used to modify the flexural modulus and improve the material’s flexibility. Plasticizers are commonly used in materials like TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) to achieve specific mechanical properties.
Flame Retardants:
Adding a Flame retardant limits or inhibits the flammability of the final plastic product. They are essential for meeting flammability standards and ensuring the safety of products in certain applications. Flame retardants come in various ratings such as HB, V0, and V1.
UV Stabilizers:
UV stabilizers protect plastic materials from degradation caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly sunlight. Adding a stabilizer helps to maintain the material’s color and mechanical properties over time.
Antistatic Additives:
These additives reduce the tendency of the plastic to build up static charges by altering its conductivity or resistivity. They are crucial in applications where electrostatic discharge needs to be controlled.
Blowing Agents:
Blowing agents initiate a chemical reaction that creates air pockets within the plastic during injection molding. This results in a cellular structure that reduces material consumption, part weight, and sink marks.
Internal Lubricants:
Internal lubricants enhance the material’s flow characteristics during molding, making it more slippery. They are beneficial for complex parts with intricate geometries.
Release Agents:
Release agents improve the ejection of parts from molds, reducing the risk of drag marks or scratches on the finished product. They are especially useful for parts with insufficient draft angles.
Antimicrobials:
Antimicrobial additives increase a plastic’s resistance to microbial growth, making them suitable for applications where hygiene is critical, such as in the medical industry.
Fillers:
Fillers are materials like glass fibers, carbon fibers, talc, ceramics, or organic substances / sustainable solutions that are added to enhance the strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability of the plastic. They create a reinforced structure within the material.
Benefits of Plastic Additives and Fillers in Injection Molding
The incorporation of plastic additives and fillers offers several significant benefits in injection molding:
Improved Material Properties: Additives can enhance the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of the base resin, allowing it to meet specific performance requirements.
Cost Efficiency: By reducing material consumption or improving processing efficiency, additives and fillers can contribute to cost savings in the manufacturing process.
Customization: Additives provide flexibility in achieving desired colors, appearances, or performance characteristics for the final product.
Compliance: Additives like flame retardants help products meet regulatory and safety standards.
Enhanced Aesthetics: Colorants and appearance-modifying additives improve the visual appeal of plastic parts.
Weight Reduction: Fillers can reduce the weight of parts while maintaining their strength and rigidity.
Plastic additives and fillers play a pivotal role in enhancing the versatility, performance, and appearance of the finished good or plastic product. Expert plastic injection molding companies can achieve a wide range of advanced materials with select properties and characteristics by selecting the right plastic additives and fillers. Whether it’s altering colors, improving flexibility, or meeting specific regulatory requirements, these compounds are indispensable tools in the world of injection molding, enabling the production of customized high-performance plastic products.